A guide to understanding cryptography in blockchain technology
Source: Crush Crypto
The creation of Bitcoin in 2009 marked the birth of the first digital currency to achieve widespread adoption across the globe. However, the concept of a secure digital currency has been around since the 1980s and there have been many previous attempts that directly inspired Satoshi Nakamoto’s creation of Bitcoin.
- Encryption: Encoding text into an unreadable format.
- Decryption: Reserving encryption – converting a jumbled message into its original form.
- Cipher: An algorithm for performing encryption or decryption, usually a well-defined set of steps that can be followed.
Cryptography before the modern age was synonymous to encryption – the process of converting information from a readable format to something that makes no sense. Encryption techniques date back as far as the ancient Egyptians, and have roots spanning all throughout history.
For example, the Caesar Cipher is a famous cipher used by Julius Caesar to securely communicate with his generals. The cipher “shifts” each letter in a message by a certain amount – with a shift of 2, A would become C, B would become D, and so on.
Blockchain technology makes use of cryptography in multiple different ways – for wallets, transactions, security, and privacy-preserving protocols. This article will cover some important cryptography topics that relate to blockchain technology including public-key cryptography, hashing, and Merkle trees.
Public-key cryptography (also called asymmetric cryptography) is a cryptographic system that uses a pair of keys – a public key and a private key. The public key may be widely distributed, but the private key is meant to be known only by its owner. Keys are always created in a pair – every public key must have a corresponding private key.
Public-key cryptography is most often used for encrypting messages between two people or two computers in a secure way. Anyone can use someone’s public key to encrypt a message, but once encrypted, the only way to decrypt that message is by using the corresponding private key.
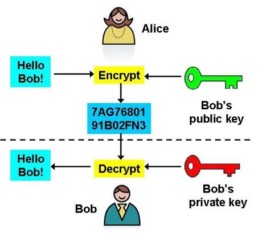
Let’s say Alice wants to send an encrypted message to Bob. It would work like this:
- Alice uses Bob’s public key to encrypt the message.
- Alice sends the encrypted message to Bob – if a third party intercepted it, all they would see is random numbers and letters.
- Bob uses his private key to decrypt and read the message.
A diagram illustrating this process is shown below:

Public-key cryptography is a fundamental element of blockchain technology – it is the underlying technology for wallets and transactions. When a user creates a wallet on a blockchain, they are generating a public-private key pair.
The address of that wallet, or how it’s represented on the blockchain, is a string of numbers and letters generated from the public key. Due to the nature of blockchain technology, this address is public to everyone and can be used to check the balance in that wallet or send coins to it.
The private key associated with a wallet is how to prove ownership and control the wallet. It is the only way to send coins out of it, and a lost private key means the coins inside will be stuck there forever.
A transaction on the blockchain is nothing more than a broadcasted message that essentially says, “Take X coins from my wallet and credit X coins into another wallet”. Once confirmed, the transaction is immutably written into the ledger, and the balances are updated.
However, this transaction message requires a signature from the private key of the sending wallet to be valid. After broadcasting, anyone can use that wallet’s public key to ensure the digital signature coming from the private key is authentic. This is one role of block validators before they add any transaction (i.e. message) to the blockchain.
Cryptographic hashing is another fundamental piece of blockchain technology and is directly responsible for producing immutability – one of blockchain’s most...
TRON Showing Bullish Trading Signs
TRON Symbol TRX | Decentralize The Web
The TRON Protocol, one of the largest blockchain based operating systems in the world, offers ... TRX consistently handles 2,000 transactions per second, 24x7.
Author: Ken Chigbo / Source: Hacked: Hacking Finance
TRON (TRX/USD) closed 2018 with strength relative to the last couple of months. It is currently trading around $0.0208. At this price level, the market is up more than 90% from its 2018 low of $0.0111 on November 25.
This huge surge in less than one month is more than enough reason for many traders to be bullish on TRON. However, one must also consider that when the market bottomed out, it lost close to 90% of its value from the 2018 peak of $0.10041. Thus, it would also make sense to say that the recent bounce is nothing more than a relief rally.
That is why it is important to examine the market closely to see whether TRON has more upside potential. We did that for you and what we saw was promising. In this article, we reveal how TRON is showing bullish signs.
Structure Resembles Market Leader
In any asset class, whether it be equities or cryptocurrencies, there are some instances when a market leader emerges and then everyone else follows its direction. For example, Apple Inc. was down big yesterday, January 3. Notice how many tech stocks followed suit.
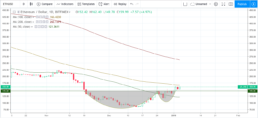
As for cryptocurrencies, the clear market leader right now is Ethereum (ETH/USD). It is currently trading around $160 to put the market up by over 95% from its 2018 low of $83. More importantly, Ethereum has taken out firm resistance of $145. This triggered the breakout from the cup and handle pattern.

ETH/USD daily chart
TRON appears to be following the same pattern. It established...
Top 8 Women Entrepreneurs In Cryptocurrency
Nowadays, cryptocurrency and the blockchain is on the minds of many entrepreneurs and investors across the globe.
Cryptocurrencies came into existence in the year 2009 with the creation of the blockchain as a secure decentralized distributed ledger to serve as the public transaction ledger of the world's first cryptocurrency Bitcoin, that was conceived and presented by a pseudonymous individual or organization called Satoshi Nakamoto.
The blockchain that enables the building of digital assets is a growing list of records, called blocks, which are linked using cryptography. Each block contains a cryptographic hash of the previous block, a timestamp, and transaction data.
Cryptocurrency can be described as digital money that people can use as a medium of exchange without the restriction of borders or any central control.
This digital currency system is decentralized, yet highly secure as it uses the state of the art blockchain cryptography. The term decentralized implies that cryptocurrencies don’t rely on any centralized bank or monetary system to exist.
Furthermore, its digital nature enables users to buy things or to exchange it to and from anywhere across the globe without the worry of any kind of interruption from the banks.
The currency is operated and maintained by the network of users [cryptocurrency miners] instead of any central body.
The mining process is complex but it’s essential to understand that there is a limit to how much cryptocurrency can be created and there is currently no way to exceed that limit. Making it impossible to devalue cryptocurrency as it’s possible to do for paper dollars by banks or governments printing more paper currency.
There are 1500 plus different cryptocurrencies in the crypto market like Bitcoin, Ethereum and Litecoin which all have their own distinct properties and characteristics but they all follow some of the most basic cryptocurrency principle.
The bitcoin design has inspired a new significant global digital transformation layer, and opportunity for female entrepreneurs to develop applications, and blockchains which are readable by the public, and widely used by cryptocurrencies. Here is a list of the top women who are leading the cryptocurrency startup economy including Joyce Kim, Perianne Boring, Amber Baldet, Jinglan Wang, Jen Greyson, Fahima Anwar, Meltom Demirors, Raine Revere.
TRON has 50+ dApps, reaching 100M transactions in 173 Days - Justin Sun
Source: CCN
Justin Sun - Founder & CEO - Tron Foundation | Facebook | Twitter | LinkedIn
On Thursday, Justin Sun, the founder of TRON, said that the network supports more than 50 decentralized applications (dApps) and is on track to reach 80 dApps in the short-term.
#TRON now has more than 50+ Dapps. 80+ we are coming! #TRX $TRX
— Justin Sun (@justinsuntron) December 21, 2018
The statement of Sun follows a major milestone achieved by the blockchain network earlier this month, achieving 100 million transactions in 173 days, averaging 578,034 transaction per day.
Usage of TRON DApps
In August, Martin Köppelmann, the founder of Ethereum-based prediction market platform Gnosis.ph, said that an important statistic to reference in measuring the rate of growth of a smart contract protocol is the usage of dApps and the number of dApps that interact with each other.
Köppelmann said:
The numbers we care about is the usage of decentralized applications. And as a next step, the number to look out for is DAPPs that seemlessly interact with each other and draw a benefit from being on the same platform. As a side effect, ultimately the price of ETH will then be a function of the demand for the use of applications in this reliable, open, and interlinked environment.
Like Ethereum, TRON is a smart contract protocol and its value comes from its ecosystem of...
Bitcoin Is a Declaration of Monetary Independence - Nick Spanos
Source: Bitcoin Magazine
OPINION
Nick Spanos is an early adopter and innovator in the blockchain space. He is best known for launching Bitcoin Center NYC, the world’s first live cryptocurrency exchange, in 2013, right next to the New York Stock Exchange — as immortalized in the Netflix documentary “Banking on Bitcoin.” As part of Bitcoin Magazine’s series of interviews and op eds leading up to the 10th Anniversary of Bitcoin, Nick shares his thoughts an early Bitcoin adopter.
Nick Spanos - Founder - Bitcoin Center NYC Twitter | @nickspanos | LinkedIn
Before Bitcoin, I worked tirelessly for liberty-minded political candidates for many years. These candidates, the most prominent of whom was Dr. Ron Paul, spoke out against the Federal Reserve Bank because of its role in inflating the money supply which devalued the life savings of hard-working people. In almost every case, the mass media would sharply (and often unfairly) attack the image of the candidate with half-truths and misinformation, decimating our poll numbers, until they were sure that we would be defeated on Election Day. No matter how hard we worked or how much money we raised, we were no match for what I call the political bosses of today, the mainstream media.
After two decades of struggle, I thought I had wasted my life fighting unwinnable battles. Then one day, I read the Bitcoin white paper. I read it half a dozen times and I thought, “Finally, I have a weapon that cannot be destroyed on Election Day.”
Bitcoin for me is not an instrument for financial investment. Bitcoin for me is a declaration of our monetary independence.
When I started the Bitcoin Center in 2013, I had a flourishing real estate business in downtown New York. I had an established career in developing technologies for political campaigns. Because of bitcoin’s reputation in the mainstream media back then, I knew that many of my relationships would be destroyed if I emerged as a public figure in the cryptocurrency space.
When I launched the center, a press release was sent out revealing me as the founder even though I never wanted that information to go public. Immediately, concerned friends and family started calling me, asking me what I was getting myself into and wondering if I had lost my mind. Bitcoin was for illicit activities on the internet, they told me. This is nothing but video game money, said others.
My life mission of personal freedom was more powerful than anything anyone could ever say to me.
I knew I had to bring Bitcoin out of the back alleys and onto Wall Street for...
Digital asset hedge fund wagers $1 million on crypto to outperform stock market this decade
Source: CCN

Morgan Creek puts up a $1 million wager, inviting investors who believe the crypto market won’t outperform the S&P 500 to put their money where their mouth is, according to a CNBC report.
Morgan Creek operates an index fund called the Digital Asset Index Fund, in partnership with Bitwise Asset Management. The index funds offer high net-worth investors exposure to the top cryptocurrencies by market value.
The cryptocurrency investment firm is calling the challenge the Buffett Bet 2.0, mimicking Warren Buffet’s 2007 decision to bet $1 million that the S&P 500 would do better than a group of hedge funds against asset manager Protégé Partners. Buffet ended up winning the bet before donating his earnings to charity. Likewise, Morgan Creek is calling on any investor who believes the S&P 500 would produce more returns than Morgan Creek’s crypto investments over a 10 year period.
Co-founder and partner at Morgan Creek, Anthony Pompliano, said whoever’s on the other side of the bet has to be either someone bullish on the index fund or someone who believes cryptos are overvalued.
“This is a combination of our outlook not only for...
Why billionaire investors remain positive on long-term trend of cryptocurrency
Source: CCN

Mike Novogratz, Jim Breyer, and Tim Draper are some of many billionaire investors in the traditional financial market who remain optimistic towards the long-term trend of digital currencies.
How are these investors able to maintain their positive stance in regards to the growth of the cryptocurrency sector following an 85 percent decline in valuation across the board?
It’s About Cycles
For the most part, high profile individual investors are able to handle severe losses in emerging asset classes and high-risk assets like cryptocurrencies such as Bitcoin (BTC) and Ethereum (ETH) because they account for a small part of their wealth and portfolios.
As is the same in real estate and other traditional markets, wealthy investors have the ability to hold onto assets and properties even during the event of an unexpected market crash or the occurrence of a bear market.
| Funding in as Little as 24 Hours. Rates as Low as 6.5% |
|
|
|
| We've Arranged Over $2 Billion in Small Business Loans and Financings |
|
| Biz2Credit | |
| Learn more |
But, normal retail investors and individual traders who need quick cash to cover day-to-day operations and expenses have no other option but to sell most of the high-risk assets they hold in their portfolios.

In bear markets, retail traders often suffer a significant loss because they are unable to handle an...
EOS blockchain deep dive
Source: Crush Crypto

EOS is a blockchain-based development platform designed for building decentralized applications (dApps). Developers can write and deploy smart contracts that power dApps and decentralized autonomous organizations (DAOs).
The platform has a native token with the ticker EOS. EOS tokens were first released as an ERC20 token on the Ethereum blockchain, but a main-net token swap occurred after EOS Version 1.0 was deployed in June 2018.
EOS is often referred to as a decentralized operating system, where holding tokens represents a proportional share in the network bandwidth, storage, and computational resources. DApp developers must stake a certain number of tokens (called RAM) to cover the resources used by their DApp, but they receive those tokens back if the DApp is taken down.
Because of this staking model, users can interact with and use dApps for free. There are also no transaction fees on the EOS network, and block producers earn rewards from newly minted tokens.
EOS was developed and launched by the software company Block.one, who released the software as free and open source. Block.one built the EOS platform to incorporate 3 major features: scalability, flexibility, and usability.
It aims to be scalable by supporting thousands of commercial scale dApps, facilitating inter-blockchain communication, and separating authentication from execution.
It aims to be flexible through the ability to freeze and fix faulty or bug-laced dApps and incorporating generalized role-based permissions.
It also aims to incorporate usability through a web toolkit for interface development, self-describing interfaces, and a declarative permission scheme.
The EOS blockchain uses a Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS) consensus mechanism with 21 block validators and integrated Byzantine fault tolerance. Delegated Proof of Stake is a consensus mechanism where blocks are validated by a pre-selected group of nodes and it allows for high transaction throughput.
Byzantine fault tolerance is the ability of a network to handle situations where nodes go down or malicious nodes broadcast faulty information. EOS is theoretically Byzantine fault tolerant because 15 out of the 21 block producers are required to confirm a transaction (a 2/3 majority).
For a more detailed discussion on Byzantine fault tolerance and the reason a 2/3 majority is important, refer to our Practical Byzantine Fault Tolerance article.
EOS transactions are typically confirmed within 1 second with a 99.9% certainty, as a new block is created every 0.5 seconds. Dan Larimer stated in an April 2018 blog post that EOS can theoretically support over 1,000 transactions per second and aims to scale to 6-8,000 transactions per second in the future.
EOS also implements a mechanism called Transaction as Proof of Stake (TaPoS), where every transaction must include part of the hash of a recent block header. TaPoS makes it difficult to forge counterfeit chains considering the counterfeit chain would not be able to migrate transactions from the legitimate chain.
- DPoS consensus mechanism: See above section.
- Parallel processing: The ability to do things in parallel on the EOS network allows for faster transaction speeds and more scalability. This is planned for implementation in future versions of EOS.
- Network flexibility: If a DApp is faulty and contains a critical bug, the elected block producers can freeze it until the issue is resolved.
- High transaction throughput: EOS can theoretically support over 1,000 transactions per second with hopes that the platform can scale even higher.
- Ownership model: Owning EOS tokens represents a proportional share of the network resources like bandwidth, storage, and processing power. Developers must prove they hold a sufficient number of tokens to create DApps on the EOS blockchain.
- No transaction fees: Sending EOS tokens to another user or using them for a DApp requires no fee.
- EOS Constitution: The Constitution is a multi-party contract entered into by members of the EOS ecosystem by virtue of their use of the platform. The Constitution has 18 articles that outline the rules and user rights governing the EOS blockchain.
- June 5, 2017: EOS Technical White Paper released.
- June 9, 2017: Draft of the EOS token sale smart contact released.
- September 14, 2017: EOS.IO Dawn 1.0 released – the first release of the EOS.IO software development kit (SDK).
- December 5, 2017: Dawn 2.0 released.
- January 13, 2018: Former Bithumb CEO Richard Jung joined Block.one as Head of Korea.
- January 16, 2018: EOS.IO Blockchain Focused Fund formed.
- January 23, 2018: Block.one and Galaxy Digital announced joint venture for $325 million EOS.IO fund.
- April 5, 2018: Dawn 3.0 released.
- April 6, 2018: Block.one signed a $200 million joint venture partnership to accelerate Asia-focused EOS ecosystem development.
- May 11, 2018: Dawn 4.0 released.
- May 31, 2018: EOS Bug Bounty Program went live.
- June 1, 2018: Version 1.0 of open source EOS blockchain software released and EOS Developer Portal went live.
- June 9, 2018: EOS main-net launched.
- July 19, 2018: EOS Version 1.1.0 released.
- August 14, 2018: EOS Version 1.2.0 released.
- September 18, 2018: EOS Version 1.3.0 released.
- October 17, 2018: EOS Version 1.4.0 released.
Block.one has committed to investing over $1 billion into projects focused on growing the EOS ecosystem through their venture capital firm EOS VC. They also host EOS hackathons around the world and fund prizes for the winning projects.
Projects can receive more information about EOS VC and find an application link here: https://vc.eos.io/about-eos-vc/
There is no updated roadmap for the future technical development of EOS.
The EOS blockchain has a native token called EOS. As of December 7, 2018, the total supply is 1,006,245,120 EOS and the circulating supply is 906,245,118 EOS.
EOS tokens represent a share in the platform’s resources – this includes bandwidth, storage capacity, and processing power. Developers who wish to build dApps that run on the EOS blockchain must prove they hold a certain number of tokens and then stake those tokens to deploy the DApp.
Application developers must stake tokens to cover the nominal cost of account creation to sign up new users for their DApp. In addition, they must stake tokens for any storage, CPU power, or bandwidth used by the user. If the developer takes the DApp down, they receive their staked tokens back.
Developers can refer to the EOS Resource Center for up-to-date staking cost calculations. Baseline costs as of December 7, 2018 are outlined...
Napston digital currency launches fully automated cryptocurrency exchange
Author: Erik Gibbs / Source: Coingeek

Tech
The Napston cryptocurrency exchange has the potential to turn the industry upside down, if it’s able to produce the results the company expects. The exchange is a fully automated platform that uses a proprietary technology, the “Distributed Artificial Neural Networks (DANN),” to make accurate market predictions. Company officials assert that the platform pools data from “thousands” of independent sources and makes trading possible for even the most inexperienced investor.
According to a press release by the company, “Napston entered the cryptocurrency space in 2013, long before it became mainstream. Over the last five years, the company has been through all the uncertainties and fluctuations of this evolving market. During this phase, Napston was serving only the larger corporate and high net worth individual customers, helping them properly structure and trade their cryptocurrency portfolios. They have spent a high percentage of profits to build the proprietary Distributed Artificial...
Understanding the blockchain is in 2 mins
Author: M Waqas Raza / Source: Hacker Noon
A friend of mine asked “Tell me about blockchain in 2 mins”
Let me give it a go!
What is it?
Blockchain technology enables peer-to-peer transactions without an intermediary while keeping all transactions data transparent in a decentralised storage and tamper-proof manner.
- It is a foundational technology.
- It provides Internet of Value (WWW provides Internet of Information).
- It enables distribution of trust in place of traditional trusted functions.
- Data or records stored in blockchain are immutable (cannot be altered).
- Its records are traceable/audit-able from origin to end.
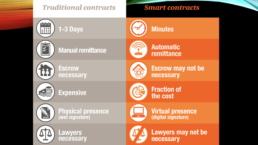
- Smart contract features enable the automatic triggering and execution of events when certain predefined conditions are met.
- When applied and working with other technologies, like Internet of Things, it will enable automatic governance.